La fonction cosinus intégral, notée , est définie par l'intégrale :
où la fonction est la fonction cosinus.
Propriétés
- La fonction est continue, infiniment dérivable sur , et
- La fonction admet le développement suivant sur : où est la constante d'Euler-Mascheroni. Ce développement permet d'étendre la fonction en une fonction analytique définie sur tout le plan complexe privé de la demi-droite des réels négatifs. La somme de la série vaut également .
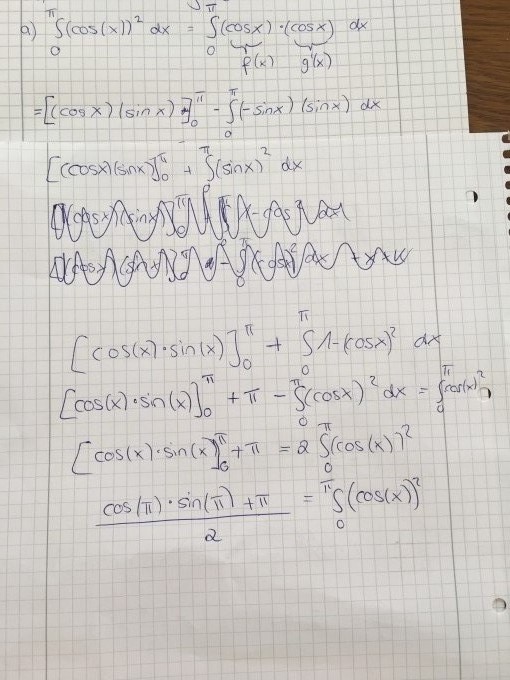
- Les primitives de Ci sont de la forme :
- .
Voir aussi
- Exponentielle intégrale
- Logarithme intégral
- Sinus intégral
Bibliographie
- Abramowitz et Stegun, Handbook of Mathematical Functions.
- (en) Eric W. Weisstein, « Cosine Integral », sur MathWorld